Introduction of Plastics
How to classify plastic?
Roughly divided into two major categories:
1. Thermoplastic plastic : It can be formed by flowing into a mold after heating. The resin molecular chains in thermoplastic plastics are all linear or branched structures. There are no chemical bonds between the molecular chains. They are softened and plasticized after heating, and hardened after cooling. , Plastic that will soften after reheating. That is, heating and cooling are used to produce a reversible physical change between liquid and solid, such as PVC, PET, PE, PP, etc.
2. Thermosetting plastic : It can soften and flow when heated for the first time, and when heated to a certain temperature, it will produce a chemical reaction called crosslinking, which becomes a three-dimensional structure, It becomes a three-dimensional structure, and it solidifies and hardens. This change is irreversible. It can no longer become soft and flow when heated again. With the help of this feature, the molding process is performed, and the plasticizing flow during the first heating is used to fill the cavity under pressure, and then solidify into a product of a certain shape and size, such as rubber, silicone, epoxy resin, melamine, unsaturated resin, etc.
1. Thermoplastic plastic : It can be formed by flowing into a mold after heating. The resin molecular chains in thermoplastic plastics are all linear or branched structures. There are no chemical bonds between the molecular chains. They are softened and plasticized after heating, and hardened after cooling. , Plastic that will soften after reheating. That is, heating and cooling are used to produce a reversible physical change between liquid and solid, such as PVC, PET, PE, PP, etc.
2. Thermosetting plastic : It can soften and flow when heated for the first time, and when heated to a certain temperature, it will produce a chemical reaction called crosslinking, which becomes a three-dimensional structure, It becomes a three-dimensional structure, and it solidifies and hardens. This change is irreversible. It can no longer become soft and flow when heated again. With the help of this feature, the molding process is performed, and the plasticizing flow during the first heating is used to fill the cavity under pressure, and then solidify into a product of a certain shape and size, such as rubber, silicone, epoxy resin, melamine, unsaturated resin, etc.
What is the difference between crystalline and amorphous plastics?
Crystalline plastic refers to the regular arrangement of macromolecules inside the plastic with a clear melting point. Regularly arranged regions are called crystalline regions, disorderly arranged regions are called amorphous regions, and the percentage of crystalline regions is called crystallinity. Generally, polymers with crystallinity above 80% are called crystalline plastics.。
1. Common crystalline plastics are: Polyethylene PE, polypropylene PP, polyamide PA6 (Nylon 6), polyamide PA66 (Nylon 66), polybutylene terephthalate PBT, polyethylene terephthalate PET, polyoxymethylene POM, etc.
2. Common amorphous plastics are :
Polystyrene PS, ABS resin, polyacrylic resin PMMA, polycarbonate PC, modified polyphenylene ether PPE, etc.
1. Common crystalline plastics are: Polyethylene PE, polypropylene PP, polyamide PA6 (Nylon 6), polyamide PA66 (Nylon 66), polybutylene terephthalate PBT, polyethylene terephthalate PET, polyoxymethylene POM, etc.
2. Common amorphous plastics are :
Polystyrene PS, ABS resin, polyacrylic resin PMMA, polycarbonate PC, modified polyphenylene ether PPE, etc.
How to distinguish common plastic products?
After purchasing plastic products, you can find the "Plastic Identification Code" printed on the shell of the product. It is a triangle composed of three clockwise rotating arrows, with a number representing each material in the middle. There are currently 7 identification codes, and the last number 7 is "other types", including acrylic, polycarbonate (PC), polylactic acid (PLA), etc., all belong to the number 7.


Development and trading of PVC compounds
Can free samples of PVC compounds be provided in the initial evaluation stage? How many quantities can be provided?
After understanding customer's product requirements, we will first recommend suitable existing specifications. If there is no suitable specification, we can also adjust and develop the formula. After both parties confirm the quality and price, we can provide free samples for customers to confirm processability and other physical properties. The quantity is reviewed according to the size of the customer's product and the number of trial molds, generally ranging from a few kilograms to 50 kilograms. Special circumstances can be dealt with case by case.
I have product development needs. What kind of PVC compounds should I choose, and can you provide assistance?
Nanya PVC compounds have complete specifications and are suitable for a variety of industrial products. Please refer to the product information and specifications on the website first, or download our company's electronic catalog for reference. We can also make customized development according to the customer's requirements. You can contact us by phone or email, or leave your needs, our engineers will provide assistance.
Is there a minimum order quantity for PVC compounds? How long is the lead time?
Generally, the MOQ is 1 ton, and it is take-to-order production, and the lead time is about two weeks. If the demand is small and the lead time is urgent, we can also find our distributors to assist you.
What are the package of PVC compounds?
There are kraft paper bags of 25KG, and jumbo bags of 600KG, 700KG, 750KG.
Use of PVC Compounds
Do PVC compounds have an expiration date?
Store PVC compounds indoors and in room temperature environment, and keep away from sunlight, humidity and heat. The recommended storage period is one year. If it expires, please check whether the color of PVC compounds have faded, whether there is precipitation or blooming on the surface, and whether the processability is different from usual. If the above condition happens, it is not recommended to use.
What is the recommended processing machine for Nanya NON-P (Non-Phthalate) medical grade PVC compounds?
The recommendations are as follows:
1.Extruder screw L/D 24~28:1
2.Compression ratio of extruder screw 2.5~3.0:1
3.Compression ratio of injection machine screw 2.0~3.0:1
If your company's machine is not in the above specifications, we can specially develop a special formula to meet the needs.
1.Extruder screw L/D 24~28:1
2.Compression ratio of extruder screw 2.5~3.0:1
3.Compression ratio of injection machine screw 2.0~3.0:1
If your company's machine is not in the above specifications, we can specially develop a special formula to meet the needs.
Does Nanya compound need to be heated and dried when used?
Generally, PVC compounds do not need special drying treatment. If there are special needs, it is recommended to use a hot air dryer at a drying temperature of 50~80℃ for 1~2 hours. The drying time should not be too long, and there should be no dead spots in the material barrel, so as to avoid the deterioration of the quality of PVC compounds after being heated for too long.
What is the chemical resistance of rigid PVC materials?
The applicability of rigid PVC materials to common chemicals is sorted out as follows:
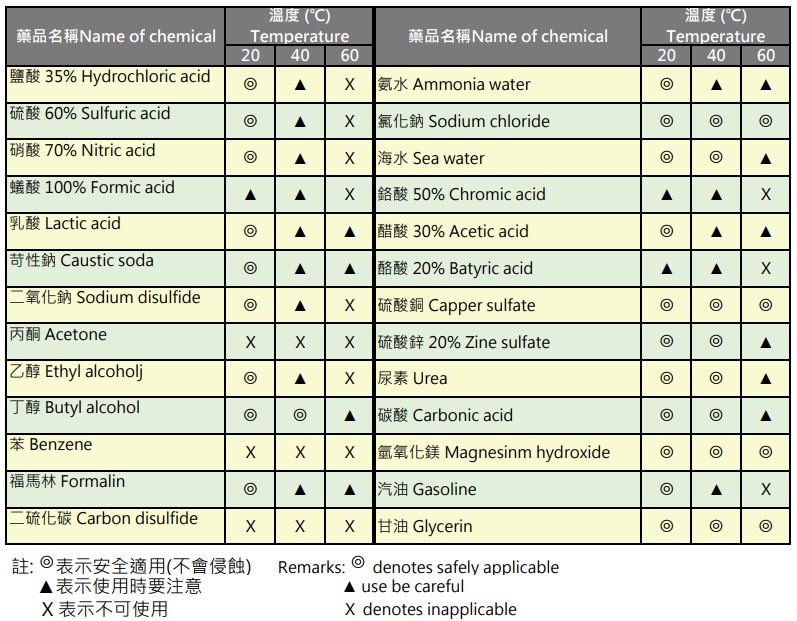
Note: Due to the different types and contents of flexible PVC plasticizers, the tolerance for chemicals varies, so reference cannot be provided.

Note: Due to the different types and contents of flexible PVC plasticizers, the tolerance for chemicals varies, so reference cannot be provided.
Has Nanya medical grade passed the biocompatibility test?
Yes, Nanya medical grade PVC compounds have passed USP(United States Pharmacopoeia) biocompatibility tests, including acute systemic toxicity, intradermal irritation, implantation tests, etc. Nanya PVC medical grade compounds have passed the USP VI grade test with more than 250 specifications. It also has tests for heavy metal analysis and physical, chemical characteristics testing, which meet the requirements of the European Pharmacopoeia to ensure safety.
What is NON-P?
NON-P refers to non-phthalate plasticizers (phthalate free). The total content of the six plasticizers (DEHP, DINP, DIDP, BBP, DBP, DNOP) restricted by the EU for flexible PVC products shall not exceed 0.1%(1000PPM) of the total weight. At present, NON-P plasticizers include DOTP, DINCH, ATBC, TOTM, etc. Nanya flexible PVC compound can use non-phthalate plasticizers (phthalate free), and comply with EU regulatory standards based on customers’ needs.
Are Non-DEHP and Non-P the same?
It is not the same. Non-DEHP means that DEHP cannot be used as a plasticizer, and Non-P is phthalate free, which means that a sulphuric acid ester plasticizer cannot be used.
Why do flexible PVC products blooming?
Pure PVC resin is not easy to process. When a sufficient amount of plasticizer molecules enters the structure of PVC resin, the PVC resin will gradually soften and be flexible. The process is called plasticization. In the plasticization process, although it involves the rearrangement of the three-dimensional structure of the PVC resin, the plasticizer molecules actually did not have any form of chemical reaction with the PVC resin, so the stability of the product after the plasticization process is not good. Improper selection of raw materials or improper production conditions may cause migration and blooming of the plasticizer.
Common nouns
What is PHR?
To make flexible PVC compounds, plasticizer is needed. Generally, the manufacture uses the PHR as the unit of measurement for the plasticizer addition, and refers to the quantity of the plasticizer matched with 100KG PVC powder.
For example: 20PHR means adding 20Kg of plasticizer per 100 Kg of PVC powder. The less plasticizer is added, the harder the plastic, and vice versa, the softer the plastic.
For example: 20PHR means adding 20Kg of plasticizer per 100 Kg of PVC powder. The less plasticizer is added, the harder the plastic, and vice versa, the softer the plastic.
What is CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride)?
CPVC is the abbreviation of Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride. Conceptually, CPVC is formed by the chlorination of a single polymer of PVC. CPVC will vary greatly due to different chlorination methods, conditions and the amount of chlorine reaction. High-performance CPVC increases the basic PVC chlorine content from 56.7% to 67-74%, while the general CPVC only limits the chlorine content to 63-69%. The increase in the chlorine content of CPVC will significantly increase the hard brittle temperature Tg of the polymer. In addition, the increase in the molecular weight of the basic PVC also results in a small increase in Tg at the same chlorine content. CPVC has relatively low cost, high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, excellent mechanical properties, flame retardant and insulation properties. Its high temperature resistance and excellent chemical resistance have been highly rated in different industrial applications. Nanya is the only manufacturer in Taiwan that can produce CPVC compounds.
What is NSF?
A group of American scientists established a non-profit civil organization based on scientific research, the National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) in 1944. The focus of the work is to concentrate on water, food, air, and the environment, which are absolutely necessary for public health, and devote efforts to the formulation of research standards and the evaluation of testing methods and other related issues. To sell products related to water, food, air and environment in the United States, the product itself or the raw materials used in it must pass NSF related inspections to obtain NSF certification. The raw materials must obtain NSF 61 certification, requiring heavy metal content standards and RVCM (Residual VCM) to ensure that materials in contact with water will not release toxic substances.
What is the significance of PVC compounds that have passed NSF certification?
Products that have been tested by NSF and meet the standards are authorized to use the NSF logo. Therefore, any authorized product with the NSF logo means that the product has been confirmed in the following aspects:
1.The ability to remove impurities as indicated in the product manual can be achieved.
2. The materials that make up the product will not add polluting ingredients to the water during the process of water treatment.
3.The product can meet the design and production process requirements.
4.The product has no structural and functional defects.
5.The certification standards shown in product advertisements, sample materials and logos are true and accurate.
For example, if the PVC compounds obtain NSF 61 certification, it means that the PVC compounds have passed the heavy metal content standard and RVCM (residual VCM) testing to ensure that the products will not release toxic substances in contact with water.
1.The ability to remove impurities as indicated in the product manual can be achieved.
2. The materials that make up the product will not add polluting ingredients to the water during the process of water treatment.
3.The product can meet the design and production process requirements.
4.The product has no structural and functional defects.
5.The certification standards shown in product advertisements, sample materials and logos are true and accurate.
For example, if the PVC compounds obtain NSF 61 certification, it means that the PVC compounds have passed the heavy metal content standard and RVCM (residual VCM) testing to ensure that the products will not release toxic substances in contact with water.
What is FDA?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is a federal government agency directly under the jurisdiction of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Its main function is to be responsible for the supervision and management of food, dietary supplements, drugs, vaccines, biomedical preparations, blood preparations, medical equipment, radiological equipment, veterinary drugs and cosmetics produced and imported in the United States. It is also responsible for the implementation of Article 361 of the Public Health Service Act, including inspections of public health conditions and interstate travel and transportation, control of possible diseases in many products, and so on.
What is DMF?
DMF refers to the drug master file. If the PVC compounds used by the manufacturer have obtained DMF, the raw material of the product can be directly quoted in the FILE NUMBER of the PVC compounds during the listing review, so there is no need to time-consuming sorting. And obtaining the DMF from the US FDA shows that the supplier's quality assurance system, risk management, and raw material quality have reached international standards. Therefore, when looking for material sources, international medical manufacturers will go to the FDA to check the information of the registered DMF. Currently, Nanya medical compounds have obtained the DMF registration with the registration number of 26526.
What is USP?
USP is the abbreviation of United States Pharmacopoeia. The United States Pharmacopoeia is a comprehensive set of quality control standards for American drugs (including APIs and preparations). It is updated and republished by the United States Pharmacopoeia Commission every year. It is the regulatory code of conduct of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the U.S. Narcotics Control Administration. It is also the official pharmacopoeia of the U.S. and several other countries. Therefore, when there are differences in the methods of identification, detection, and purity determination of the drugs and excipients included in it, the methods stated in the United States Pharmacopeia will have legal effect. It also sets biocompatibility test specifications for the raw materials used in medical products, such as acute cell toxicity, subcutaneous irritation, implantation tests, etc. Nanya PVC medical compounds have passed the USP VI level test with more than 250 specifications.
What is RoHS 2.0?
Restriction of Hazardous Substances has banned the use of four heavy metals including lead, cadmium, mercury, and hexavalent chromium and two brominated flame retardants, PBB and PBDE, in electronic and electrical equipment since July 2006. The European Union revised Directive 2011/65/EU on March 31, 2015, and issued Directive (EU) 2015/863, which pointed out that the four plasticizers of DEHP, BBP, DBP and DIBP were added to the list. In short, the 10 controlled substances regulated by RoHS 2.0 are Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr6+, PBBs, PBDEs, DEHP, BBP, DBP, and DIBP. The control standards are as follows:
You can directly check the latest news on the International Chemical Policy Promotion Network of the Industrial Bureau of the Ministry of Economic Affairs.
| Restricted substance | Content limit (ppm) |
|---|---|
| Pb | 1000 |
| Hg | 1000 |
| Cd | 100 |
| Cr 6+ | 1000 |
| PBBs | 1000 |
| PBDEs | 1000 |
| DEHP | 1000 |
| BBP | 1000 |
| DBP | 1000 |
| DIBP | 1000 |
You can directly check the latest news on the International Chemical Policy Promotion Network of the Industrial Bureau of the Ministry of Economic Affairs.
What is REACH?
REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) registers, evaluates, authorizes and controls chemical substances used in products sold in EU countries.
You can directly check the latest news on the International Chemical Policy Promotion Network of the Industrial Bureau of the Ministry of Economic Affairs.
You can directly check the latest news on the International Chemical Policy Promotion Network of the Industrial Bureau of the Ministry of Economic Affairs.